In Poland, banking of hematopoietic stem cells from cord blood and tissue stem cells from the umbilical cord has been available for many years. From April 2024, Parents expecting the birth of a child can also secure the entire placenta. Otherwise, it is disposed of irretrievably by the hospital. However, priceless stem cells are lost along with it.
Properties of tissue stem cells from placenta
During delivery, in addition to hematopoietic stem cells from umbilical cord blood, it is also possible to obtain tissue stem cells. These are contained in the umbilical cord and placenta. These cells, called mesenchymal stem cells, can transform into, among other things: cartilage tissue, bone tissue or nerve tissue. Thanks to their valuable properties, they have applications in regenerative medicine.
Securing both the umbilical cord and placenta during delivery significantly expands the range of therapies that the family can use in the future, if needed.
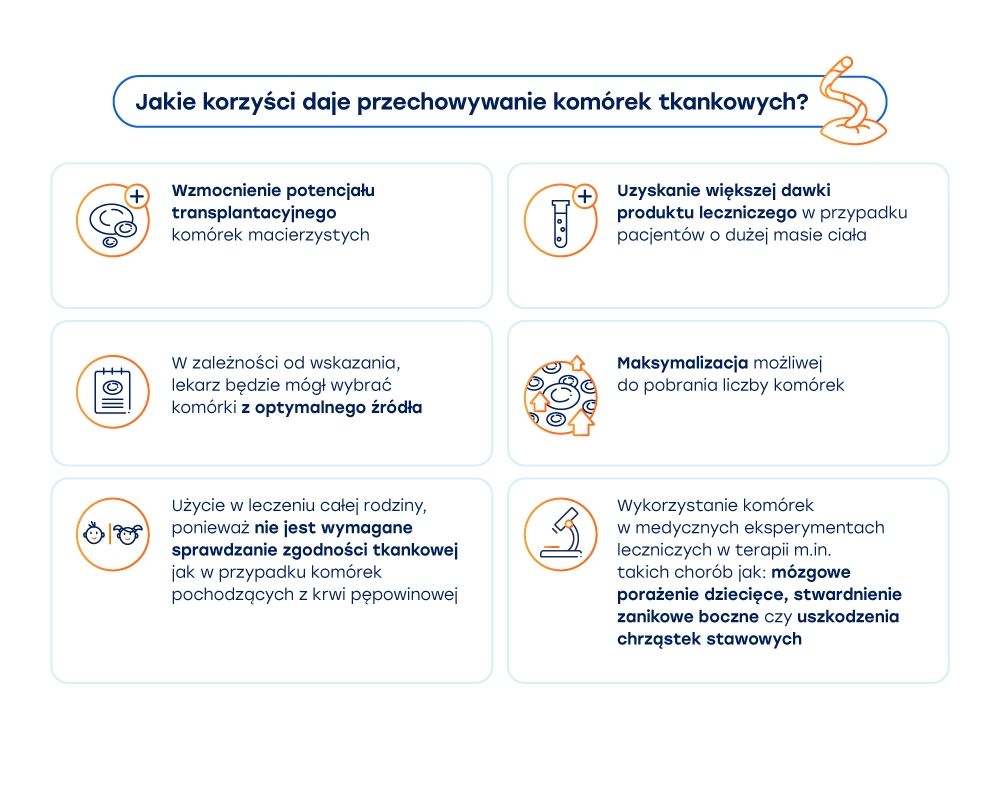
Tissue stem cells from the umbilical cord and placenta can benefit the child from whom they were collected, siblings, as well as Parents and Grandparents (provided that they are HLA tissue compatible).
What does the placenta retrieval look like?
Placenta collection is only available at the Polish Stem Cell Bank, with the Platinum variant.
Parents, after signing the contract, receive a special collection kit, with which they go to the delivery room, where a trained midwife, after collecting cord blood, umbilical cord at the end, collects the placenta and places it in a special container with saline.
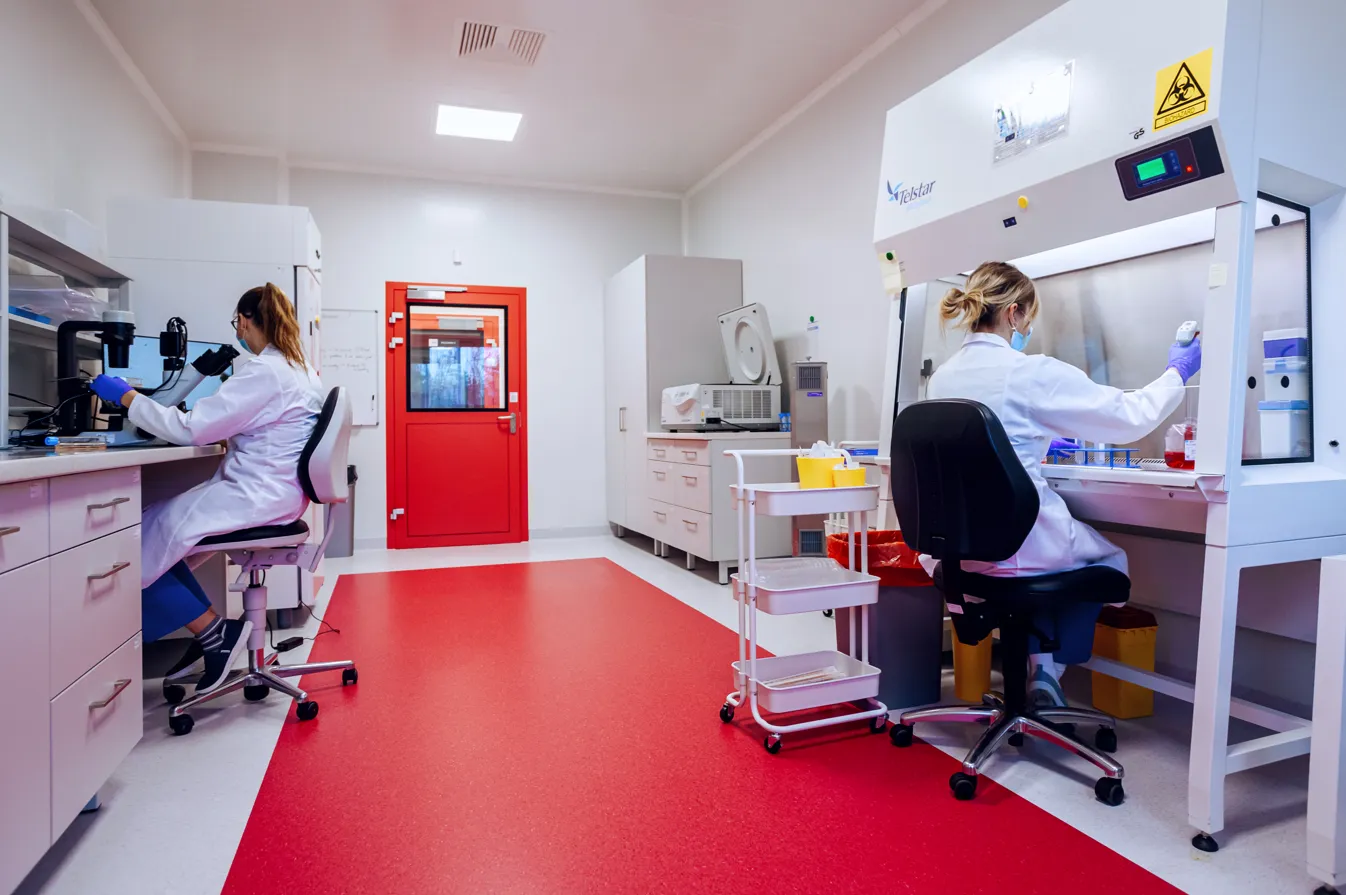
The collection set is then transported to the central laboratory of the Polish Stem Cell Bank in Warsaw, where, among other things. Placental tissues are examined and prepared, and then frozen. The material is stored indefinitely in liquid nitrogen vapor at temperatures below 176 degrees Celsius.
Rate this article:










