Cardiotocography is one of the basic tests performed on all women at the end of pregnancy and during labor. It is essential for monitoring the baby’s well-being. It also allows doctors to observe a record of a woman’s uterine contractions during labor. Is it possible to perform an OCG on your own at home? How does one read his record?
KTG – what does it consist of?
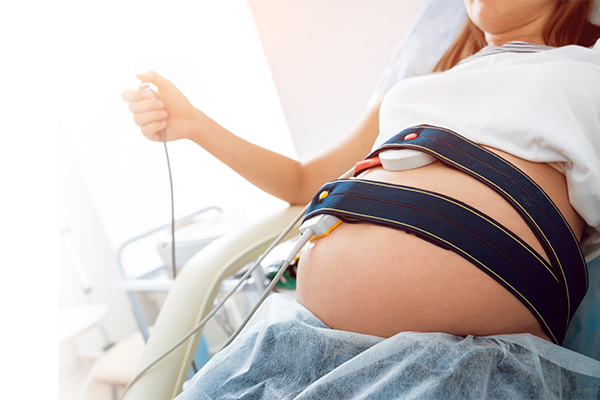
Cardiotocography is the simultaneous recording of fetal heart rate (FHR- fetal heart rate) and uterine contraction activity. This allows you to monitor the baby’s condition and emerging contractions, as well as the interdependence of the two parameters.
Two special heads – pelvises – are applied to the abdomen, previously lubricating them with ultrasound gel to allow recording of uterine contractions and the baby’s heart activity. A record appears on the device’s screen and is usually printed on the fly, too.
A heart rate between 110-160 beats per minute is considered the baby’s baseline heart rate on KTG. This is normocardia. If the child’s heart beats more than 160 times per minute we are dealing with tachycardia. Some of its causes include maternal nervousness, maternal fever, fetal infection and fetal anemia. It can also occur if the pregnant woman smoked cigarettes during pregnancy. When a child’s heart rate drops below 110 in one minute, the condition is called bradycardia. It is due to fetal hypoxia, clamping of the umbilical cord, or stimulation of the vagus nerve during the insertion of the head, the so-called “head”. Gaussian symptom.
When is cardiotocography performed?
If the pregnancy is progressing normally, an OCG is not performed until the due date. For conditions occurring during the course of pregnancy, this test is ordered in the earlier weeks. If a woman suffers from diabetes, hypertension or kidney disease, for example, the KTG test is performed from 36. Week of pregnancy once a week.
When a pregnant woman is admitted to the hospital for the onset of labor she usually has an OCG test performed in the emergency room. This is also the moment when the cord blood collection kit is transferred to the delivery room where the woman will give birth. It is a good idea to take such a kit to the hospital with you to collect the baby’s cord blood. Check out: https://www.pbkm.pl/komorki-macierzyste/dlaczego-warto
KTG is also performed during labor. In some cases, a permanent record is required, such as with an epidural, because the woman in labor then feels the incoming contractions less keenly. An OCG test is also usually performed after the insertion of a Foley catheter, aimed at preinducing labor.
Accelerations and decelerations
Specialized vocabulary is used in describing the cardiotocographic examination. Fluctuations in the baby’s heart rate are called oscillations. The correct notation is wave oscillation. This means that the fetal heart rate changes by 10-25 beats per minute. An oscillation in which the line becomes straight and the variability of the heart is less than 5 beats per minute is called a silent oscillation. This is an abnormal recording and can mean, for example, fetal hypoxia. Narrowed oscillation, on the other hand, can be caused, for example, by fetal sleep.
Accelerations are called transient increases in fetal heart rate (FHR) of 15 beats lasting at least 15 seconds relative to baseline. They usually accompany uterine contractions and mean that the baby is feeling well. Decelerations , on the other hand, are periodic lowering of the fetal heart rate. There is a distinction between early decelerations, which arise as a result of the baby’s head going lower and lower and stimulating the vagus nerve, and late decelerations, which are an exponent of uteroplacental failure and may indicate placental failure.
Doctors, observing the recording of oscillations, as well as the occurrence of acceleration and deceleration, monitor the baby’s well-being and, in the event of abnormalities, implement appropriate management, which may include a cesarean section or inhibition of oxytocin. These are elements of intrauterine resuscitation.
Home KTG
Recently, portable fetal heart rate detectors, which can be purchased or rented for home use, have become increasingly popular. They are completely safe, and Parents can listen to the baby’s heartbeat at any time. The results are usually sent to the midwife or doctor, who checks for any abnormalities. With home detectors, it is possible to monitor a baby’s heart function without leaving home. However, do not forget about the necessary scheduled visits for an OCG test at the hospital , especially if the scheduled date of delivery has already passed.
Also find out: Prenatal testing – what is it?
Rate this article: