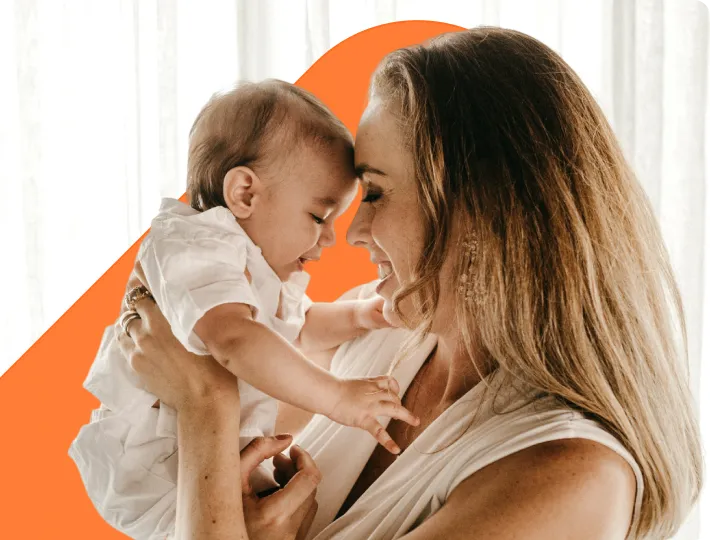
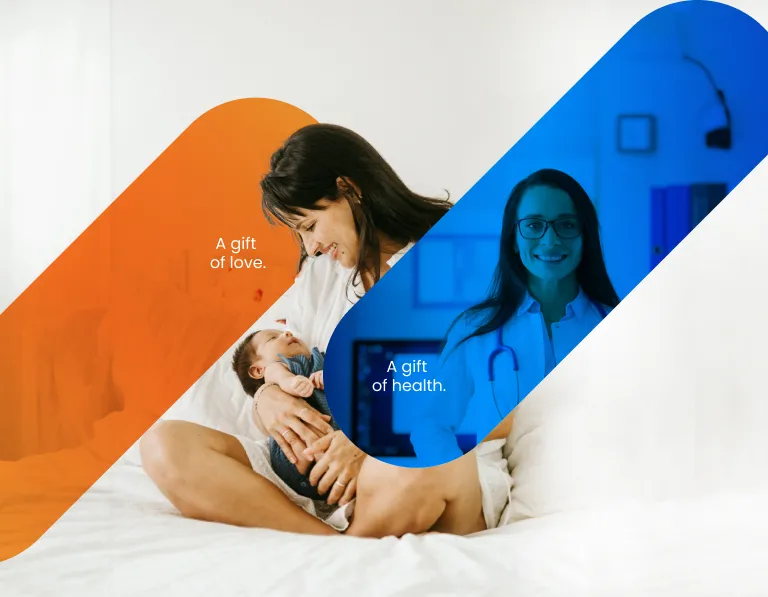
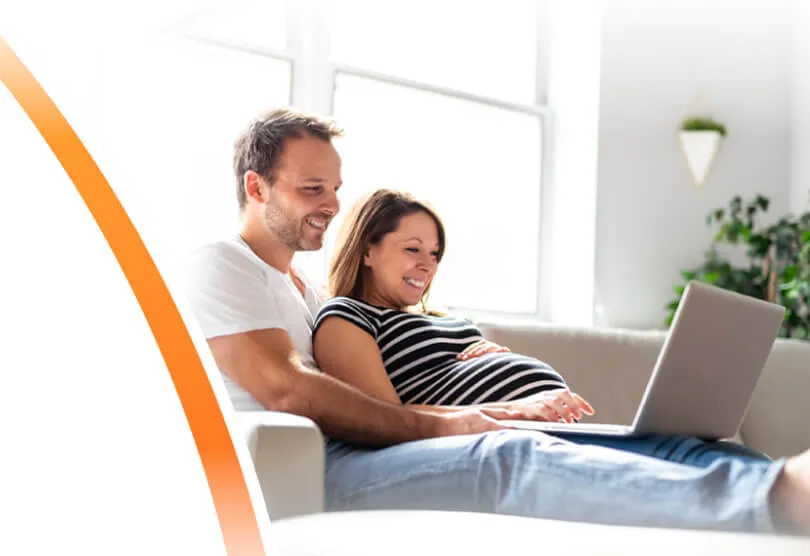
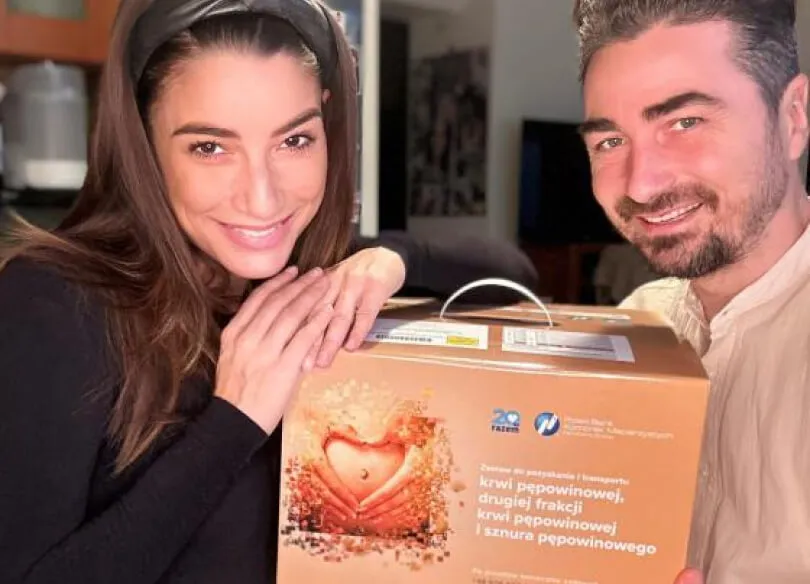
The gift of love
Securing umbilical cord blood at birth can provide your child with access to potential stem cell-based therapies in the future.
To learn more about the opportunity offered by stem cells, explore the stories of Parents who have secured cord blood.

The gift of science
Cord blood stem cells, analogous to bone marrow stem cells, are used in the treatment of nearly 80. Severe oncological and hematological diseases. Research is underway on its use in autoimmune and neurological diseases.
Check out where they have applications.
PBKM in numbers
1 000 000
stored samples
1 500
cooperating hospitals
7 130
Patients have benefited from stem cell therapy
235
use your own cord blood