Stem cells
and umbilical cord blood
Cells
Stem cells
Stem cells are used in the treatment of many diseases. Probably when you hear the words “stem cells” you associate them with bone marrow, from which they have so far been most often taken. However, an even better source of these cells is umbilical cord blood, which can be quickly and painlessly collected during childbirth. Find out what cord blood banking is and why you should opt for it!
Stem cells – what are they?
Stem cells are primary, unspecialized cells that have tremendous potential to multiply and the ability to transform into specialized cells. Thanks to these properties, they can be used in medicine to rebuild damaged tissues and cells. They are found in umbilical cord blood, bone marrow, peripheral blood after pharmacological mobilization or umbilical cord, among others.
However, the first known source of stem cells was the bone marrow (I’m sure you’ve heard of bone marrow transplantation before – it’s all about transplanting cells from the bone marrow). It is also possible to harvest stem cells from peripheral blood. On the other hand, nowadays stem cells obtained from cord blood are increasingly being used for therapy.
Stem cells are used to treat more than 80 serious diseases. Research on the use of the cells in new disease entities is constantly being conducted. Currently, they are used for treatment mainly in hematology, oncology and neurology. Diseases that can be treated with stem cells include leukemia, selected cancers, diseases of the hematopoietic and immune systems, metabolic diseases and many others. In recent years, stem cells have also been successfully used to treat autism spectrum disorder or cerebral palsy.
Stem cells – where do they come from?
For many years, the primary source of stem cells was bone marrow, because it is a widely available source – cells from the bone marrow can be harvested at almost any time in a person’s life. Unfortunately, this source comes with one basic problem – it is very difficult to find a suitable cell donor. In order for them to be used, it is necessary to obtain a suitable tissue match between the donor and the recipient. In other words, we need to find our genetic twin. To find this, we must have a match of at least 9 out of 10 HLA transplant antigens between the stem cell donor and recipient. Unfortunately, this makes finding a compatible donor very difficult, takes a lot of time, and sometimes impossible.
However, it turns out that bone marrow is not the only source of stem cells. They are also found in the cord blood remaining in the vessels of the umbilical cord after the baby is born. Therefore, they are the most primary and unspecialized stem cells, thanks to which in a situation, the search for a compatible donor , it is much easier to match donor and recipient because in the case of cord blood stem cells, a match of 4 out of 6 transplantation antigens is sufficient. Unfortunately, cord blood can be collected only once in a lifetime, so when deciding to have a child, it is worth thinking about the possibility of cord blood banking.
What is cord blood?
Umbilical cord blood is the blood that remains in the umbilical cord and placenta after birth and after the baby is unbuttoned. It is a valuable source of stem cells. Until recently, it was treated as medical “waste” and disposed of along with the placenta and umbilical cord. Nowadays, it is collected to isolate stem cells for storage and later use in treatment.
Stem cells from collected umbilical cord blood (a.k.a. hematopoietic cells), like those from bone marrow, can be transplanted to rebuild the hematopoietic and immune systems, and show greater efficacy in doing so than cells obtained from adult donors. They can be used for both autologous transplants (in which case the donor is the recipient of the harvested cells) and allogeneic transplants (the recipient gets the cells from another person, such as family transplants).
Thanks to the superiority of cells from cord blood over those from bone marrow, they are increasingly used in medical treatment and even in life-saving situations. In addition, thanks to cord blood storage, the time to start possible treatment is shortened. There is no need to search for a donor as in the case of bone marrow, since stem cells collected at birth are used in case of illness.
Comparison of sources of hematopoietic stem cells
Umbilical cord blood
Bone marrow
Time and ease of downloading
collection takes a few minutes during labor, is non-invasive and safe
collection takes a minimum of several tens of minutes by puncturing the hip bone plates during surgery under general or epidural anesthesia
Required compatibility for transplantation
it is easier to match the recipient with the donor, because the compatibility of 4 transplant antigens out of 6 tested in the so-called HLA system is required
it is more difficult to match the recipient with the donor, because a high compatibility of transplant antigens is required
– As many as 9 out of 10 in the so-called HLA system
Transplant availability
Cord blood, once deposited in the bank, is available for transplantation and awaits a recipient
The bone marrow must be collected from a donor who, even if registered in the registry, must volunteer for the collection; the donor must be in good health for the collection to be possible
Amount of material collected
on average succeeds in obtaining enough material for a child up to 50 kg, but research into the possibilities of cell multiplication is highly developed
relatively large amount of material
What does cord blood collection look like?
Cord blood collection is a simple and non-invasive procedure. It is performed after the so-called unbuttoning of the baby from the remaining part of the umbilical cord at the placenta. The entire procedure is completely safe for the baby as well as the mother.
Usually the collection is performed by a trained midwife, using a special collection kit provided to the hospital by the Parents, immediately before the birth. After collection, the secured cord blood is collected from the hospital and transported to the stem cell bank laboratory by a specialized courier service.
Storage of umbilical cord blood
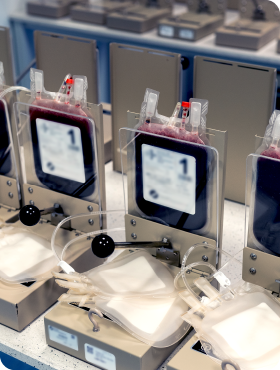
Stem cells from cord blood and umbilical cord are stored in liquid nitrogen vapor, at temperatures below -176 degrees Celsius. Under such conditions, stem cells can be stored virtually indefinitely without fear of losing their valuable properties.
Umbilical cord and placenta
In addition to hematopoietic stem cells from umbilical cord blood during delivery, it is also possible to obtain tissue stem cells. These are contained in the umbilical cord and placenta. These cells are so-called mesenchymal stem cells and their characteristic feature is that they can transform into, among other things: cartilage tissue, bone tissue or nerve tissue. Thanks to their values, they have applications in regenerative medicine.
The umbilical cord and placenta can be obtained very easily after delivery. The doctor or midwife cuts off a piece of umbilical cord (10-15 cm long) of the umbilical cord and places it in a special container. In a second container, the entire placenta is placed.
In the laboratory, the tissues of the umbilical cord and placenta are examined and prepared, and then frozen.
Securing both materials significantly expands the range of therapies that the family can use in the future, if necessary.
Umbilical cord and placenta cell procurement service is available only at the Polish Stem Cell Bank. The umbilical cord can be secured by choosing the Blue and Platinum variants. The placenta, on the other hand, can be retrieved thanks to the Platinum variant.
How do you secure biological material at PBKM?
If you want to bank stem cells, you will need to visit a family stem cell bank to sign a contract and pick up a cord blood collection kit to take with you to the delivery room. During delivery, the kit should be given to the midwife or doctor, who will collect the cord blood. Regardless of whether the birth is by natural childbirth or Caesarean section, it is possible to collect cord blood even in the case of the so-called late unbirth.
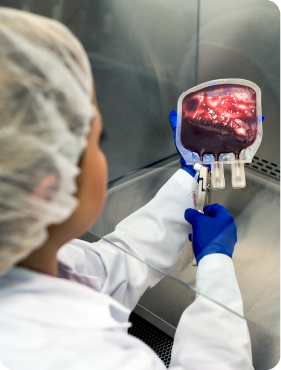
Umbilical cord blood collection is safe and painless for both mother and baby. After the blood is collected by the midwife, the material is properly secured and transported to the laboratory, where it is subjected to tests for, among other things, the presence of viruses, bacteria and fungi. After examination, the stem cells are stored in liquid nitrogen vapor at temperatures below -176 degrees, so they do not lose their unique properties and can be used at any time in the future.
In Poland, stem cell transplants are possible in several centers, including Gdansk, Bydgoszcz, Warsaw, Wroclaw and Krakow. What’s more, standard transplants are reimbursed by the National Health Fund in Poland.
-
1
After signing the contract, you have 2 days to deposit the prenatal fee in your individual account.
-
2
We send a courier to you with a kit for collecting biological material.
-
3
Keep the kit together with your delivery bag. Take it with you to the hospital. Do not open it! The kit must be originally sealed to be used. At the delivery room, hand it to the midwife.
-
4
After collection, the material is collected from the hospital by dedicated medical transport and delivered to the PBKM laboratory, where it is then tested and frozen.
-
5
Testing of the material takes 6 to 8 weeks. Once we are sure that the material is eligible for storage, final test results and a Certificate confirming the storage of stem cells will appear on www.pbkm.pl in the “My PBKM” panel
The use of stem cells – pros and cons
Cord blood banking is becoming more and more popular every year. It is hardly surprising – more and more Parents-to-be appreciate the role played by cord blood and stem cells derived from it in modern medicine.
Are there any arguments against cord blood banking?
Of course it is! One may encounter the statement that the volume of cord blood collected at birth and the number of cells in it are sufficient to treat a person weighing 40 to 50 kilograms, which may be a limitation in treatment…. However, PBKM’s experience shows that the amount of stem cells found in cord blood is an individual issue that is beyond anyone’s control, and the number of cells until the moment of collection is unknown. At PBKM we also store portions with enough cells for patients over 100 kg of body weight . It is also important to remember that on April 17, 2023. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a cord blood stem cell multiplication product in the United States. In Europe, the EMA (i.e., the European Medicines Agency) is also reviewing the application, and we expect that the technology will soon be available to patients in Europe as well. As a result, the amount of cells stored will not matter, but whether they are stored at all.
It may also turn out at some stage of the disease that transplantation of own cells from cord blood will not be possible, and instead it will become necessary to use cells from another donor. It should also be remembered despite the growing number of indications, stem cells are not applicable to all diseases, the collection and banking of cord blood is not reimbursed by the National Health Service, so Parents must bear the costs themselves. As well as there are health contraindications to cord blood donation.